Doughnut maker
From DDL Wiki
(→Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)) |
(→Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)) |
||
| Line 331: | Line 331: | ||
| "Drive gear 2" | | "Drive gear 2" | ||
*Translates motion to conveyor assembly | *Translates motion to conveyor assembly | ||
| - | | | + | | Fracture |
| - | | | + | | Conveyor belt system unable to move |
| - | | | + | | 8 || Improper manufacturing || 1 || || 1 || 8 || Introduce quality control measures on conveyor assembly ||Manufacturing|| None || 8 || 1 || 1 || 8 |
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 20:49, 16 September 2009
Contents |
Executive Summary
Bill of Materials
Main Components
Additional Parts
| Screws |
|---|

|
| Nuts and Washers |

|
Assembly Diagrams
| Dough Dispenser Cup Assembly |
|---|

|
| Dispenser Motor and Conveyor Motor Assembly |
 
|

|
| Dispenser Motor and Conveyor Motor Assembly Schematic |

|
| Conveyor Belt Assembly |

|
| Cooking Oil Assembly |
 
|
| Exterior Panel Assembly |

|
Major Stakeholders and Needs
Usage and Usability
Mechanical Function
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
| Part # | Item and Function | Failure Mode | Effects of Failure | S | Causes of Failure | O | Design Controls | D | RPN | Recommended Actions | Responsibility and Deadline | Actions Taken | S | O | D | RPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | "Dispenser spring"
| Deformed spring (too long/short) | Unable to fully open/close causing incorrect dough dispensing | 7 | Improper manufacturing | 2 | Inspecting dispenser spring | 2 | 28 | Introduce quality control measures to ascertain accurate spring dimension | Manufacturing and Quality Control | None | 7 | 2 | 2 | 28 |
| 002 | "Dispenser support"
| Warped | Dispenser plunger moving at angle disrupting dough shaping | 6 | Improper manufacturing | 2 | Inspecting dispenser support or dispenser plunger | 2 | 24 | Introduce quality control measures to ascertain dispenser quality | Manufacturing and Quality Control | None | 6 | 2 | 2 | 24 |
| 003 | "Dispenser plunger"
| Cracked | Dough unable to be pushed into system | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Inspecting dispenser assembly | 1 | 8 | Introduce quality control to ascertain dispenser quality | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 005 | "Dispenser stop"
| Leaking or cracked | Dough seeps from dispenser cup to machine | 6 | Improper manufacturing | 3 | Inspect dispenser assembly for leaks | 3 | 54 | Introduce quality control measures to ascertain dispenser quality | Manufacturing and Quality Control | None | 6 | 3 | 3 | 54 |
| 006 | "Dispenser cup"
| Cracked | Dough seeps from dispenser cup to machine | 6 | Improper manufacturing | 3 | Inspect dispenser assembly for leaks | 2 | 36 | Introduce quality control measures to ascertain dispenser quality | Manufacturing and Quality Control | None | 6 | 3 | 2 | 36 |
| 007 | "Switch cover"
| Warped | Misalignment of components | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Specify process, Material selection | 1 | 8 | None | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Fractured | Exposure / Misalignment of components | 8 | Improper handling | 2 | Material Selection, Packaging | 2 | 32 | Drop test with and without packaging | Reliability | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 | ||
| 008-010 | "Dispenser motor assembly"
| Motor operates too fast | Insufficient dough released from dispenser | 6 | Poor design, motor rotates too quickly | 9 | Lab test with various motor rotational outputs | 5 | 270 | Redesign is necessary. Alternative motor speed or alternate motor | Research and development | None | 6 | 9 | 5 | 270 |
| Rotational output (part 11) too small | 6 | Poor design, part too small to release sufficient dough | 9 | Lab test with various sized parts | 5 | 270 | Redesign is necessary. Larger sized rotational output (part 011) | Research and development | None | 6 | 9 | 5 | 270
| |||
| 011 | "Dispenser motor housing"
| Fractured | Motor is moved off position, disrupting dispensing process | 7 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Material selection, placement | 3 | 21 | Introduce quality control actions to check dispenser motor assembly | Reliability | None | 7 | 1 | 3 | 21 |
| 012 | "Dispenser switch 1"
| Sticking | Plunger stays open, dough pours into oil tub | 8 | Improper manufacturing or assembling | 1 | Inspect control systems | 5 | 40 | Take quality control actions or may redesign for extra clearance | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 5 | 40 |
| 013 | "Dispenser switch 2"
Halts the dispensing process | Sticking | Plunger does not open, no dough released | 8 | Improper manufacturing or assembling | 1 | Inspect control system | 5 | 40 | Take quality control actions or may redesign for extra clearance | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 5 | 40 |
| 014 | "Dispenser switch housing"
| Fractured | Plunger stays open/closed | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Inspect dispenser motor assembly | 2 | 16 | Introduce quality control measures on dispenser motor assembly | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 2 | 16 |
| 018 | "Conveyor belt motor"
| Conveyor belt assembly moves too slow | Doughnuts take a very long time to move through system | 4 | Motor rotates too slowly | 8 | Lab test with different motor speeds | 5 | 160 | Purchase more powerful motor, redesign for smaller drive gears | Research and development | None | 4 | 8 | 5 | 160 |
| 019 | "Drive gear 2"
| Fracture | Conveyor belt system unable to move | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | 1 | 8 | Introduce quality control measures on conveyor assembly | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 | |
| 023 | "Wire guide"
| Dislocating from position | Wires come into contact with oil bath | 9 | Improper handling | 1 | Material selection, packaging | 1 | 9 | Drop test with and without packaging | Reliability | None | 9 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| 024 | "Power jack"
| Short circuit | Unable to function | 8 | Internal problem | 1 | Choose reliable supplier | 4 | 32 | Test completed units before distribution | Assembly | None | 8 | 1 | 4 | 32 |
| 026 | "Belt motor gear"
| Fractured | Conveyor belt unable to move | 8 | Improper handling | 2 | Material selection, packaging | 2 | 32 | Drop test with and without packaging | Reliability | None | 8 | 2 | 2 | 32 |
| 027 | "Conveyor belt link assembly"
| Fracture | Doughnut unable to move through system, machine unable to perform function | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Inspect conveyor belt assembly | 4 | 32 | Introduce quality control measures on conveyor assembly | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 4 | 32 |
| 028 | "Doughnut carriage assembly"
| Bends too easily | Contributes to doughnut being unable to flip | 5 | Poor design, part too flexible | 9 | Lab test different materials with various flexiblities | 4 | 180 | Redesign using a less flexible material | Research and development | None | 5 | 9 | 4 | 180 |
| 030-031 | "Conveyor belt gear"
| Fracture | Conveyor belt system unable to move | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Inspect conveyor belt assembly | 1 | 8 | Introduce quality control measures on conveyor assembly | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 034 | "Belt guides"
| Fracture | Conveyor belt system unable to move | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Inspect conveyor belt assembly | 1 | 8 | Introduce quality control measures on conveyor assembly | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 036 & 039 | "Oil bath assembly"
| Flipper does not turn doughnuts | Doughnut unevenly cooked | 6 | Poor design, doughnut pushes flipper | 9 | Inspect oil bath assembly | 4 | 216 | Redesign the oil flipper by making a more rigid connection | Research and development | None | 6 | 9 | 4 | 216 |
| Oil bath temperature fluctuates too greatly | Doughnut burnt (usually) or undercooked | 5 | Oil bath diminishes too fast, temperature controller too poor | 7 | Inspect oil bath assembly | 4 | 140 | Purchase a better temperature controller | Research and development | None | 5 | 7 | 4 | 140 | ||
| Fractured/Leaking | Release of hot oil into system, possibly onto user | 9 | Improper handling | 1 | Material Selection, Packaging | 3 | 27 | Drop test with and without packaging | Reliability | None | 9 | 1 | 3 | 27 | ||
| Oil tub hard to clean | Oil stays in system and machine gets very dirty/greasy | 6 | Poor design, no access to oil tub | 9 | Inspect oil bath assembly | 5 | 270 | Redesign needed. Make removable panel to access oil tub | Research and development | None | 6 | 9 | 5 | 270 | ||
| 043-045 | "Oil drain knob assembly"
| Fracture | Oil drain system unable to function | 7 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Inspect oil drain assembly | 1 | 7 | Introduce quality control measures on oil drain assembly | Assembly | None | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7
|
| 046-048 | "Oil drain tube, clamps, and valve"
| Leaking | Hot oil released into machine and possibly onto user | 7 | Improper manufacturing | 2 | Inspect oil drain assembly | 4 | 56 | Introduce quality control measures on oil drain assembly | Assembly | None | 7 | 2 | 4 | 56
|
| 049 | "Oil collection tray"
| Warped/Deformed | Misalignment of components, improper fit | 7 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Specify process, Material selection | 1 | 7 | None | Manufacturing | None | 7 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Fractured/Leaking | Hot oil released from machine, possibly onto user | 9 | Improper handling or manufacturing | 3 | Material Selection, Packaging, Quality control measures | 4 | 108 | Drop test with and without packaging | Reliability | None | 6 | 3 | 4 | 108
| ||
| 051 - 052 | "Front and Back Panels"
| Warped | Misalignment of components, improper fit | 8 | Improper manufacturing | 1 | Specify process, Material selection | 1 | 8 | None | Manufacturing | None | 8 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Fractured | Exposure/Misalignment of components and heat release | 6 | Improper handling | 4 | Material Selection, Packaging | 4 | 96 | Drop test with and without packaging | Reliability | None | 6 | 4 | 4 | 96
| ||
| 055 | "Power cord"
| Short circuit | Unit unable to function | 8 | Cord Pinching | 2 | Set assembly process | 4 | 80 | Test completed units before distribution | Assembly | None | 8 | 2 | 4 | 64 |
| Internal cord problem | 1 | Choose reliable supplier | 4 | 32 | Test completed units before distribution | Assembly | None | 8 | 1 | 4 | 32 |
Design for Environment (DFE)
Surface Level Environmental Impact
In considering environmental implications of this appliance, it is important to consider both the direct effects (material flow) and the indirect effects (gaseous emissions) during the complete life cycle. Whereas market research demonstrated the material flow associated with consumer use, the product dissection showed the complex array of individual components and sub-assemblies required for proper function, implying that much of the material and energy consumption will occur during the manufacturing phase. An inexpensive kitchen appliance is designed to have a finite lifespan, where it becomes cheaper to replace the product than to repair it. This conclusion is justified by the excessive difficulty with which the components are removed and replaced, indicating that disposal will be a significant aspect to consider.
The direct, or visible, effects were observed during the market research. From a consumer’s perspective, this includes:
- Large amount of detergent/water/paper towels to clean, as oil gets on nearly every component of appliance
- Waste oil must be disposed of after each use
- Plastic casing gets extremely hot, leading to waste heat energy
- Only one doughnut is pulled through at a time, implying that the conveyor/heater must remain active for a much longer period of time to produce one batch, drawing much more energy
- This consumes an obscenely large amount of electricity per doughnut
- Excess dough is wasted due to the dispensing unit
- Complexity of product ensures that it can never be reasonably recycled by consumer, as it cannot be separated into plastic/metal components
The indirect effects come from further research, and will be highlighted in the following subsection of EIO-LCA.
Material Considerations
The product dissection allows us to further understand the material flow put into the product during manufacturing and assembly.
- Plastic
- Nearly the entire assembly is built of injection-molded plastic and is designed to be disposable. Non-recycled plastic will not degrade in a landfill. These parts cannot be easily disassembled for replacement. Energy is consumed (and consequently pollutants emitted) during the processing of such plastics.
- Metal
- Several crucial parts are built of metal, but they are designed to be removed and will not be recycled by the consumer. Energy is consumed in the extraction and processing of metals.
EIO-LCA Model
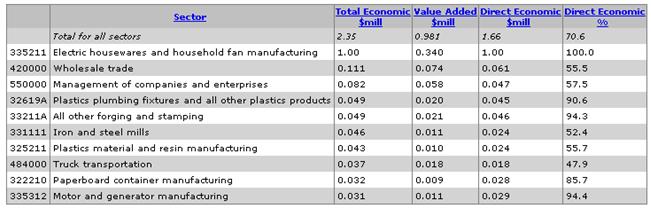
The Economic Input-Output Life Cycle Assessment (EIO-LCA) model allows us to explore the tangential sectors that will contribute to the product’s net environmental implications. An automated doughnut maker can best be described as a novelty kitchen appliance designed for a niche market; it is not expected to be found in every home. However, from an engineering and environmental impact perspective this product follows a similar life cycle to that of a toaster, coffee pot, or waffle iron. It combines injection-molded plastic pieces with a simple heating element and basic mechanical components. Therefore, while it does not explicitly fall under a category, we can make a reasonable assumption that the life cycle of our product is comparable to those found in #335211 Electric Housewares and Household Fan Manufacturing.
This model simulates environmental response values for $1,000,000 of economic input activity. We see that the majority of emissions come from power generation, which constitutes approximately 31% of all CO2 emissions. This doughnut maker, at $100 per unit, can be produced at 10,000 units per $1,000,000 input. Therefore, if 10,000 units produce 693 metric tons of CO2, this equates to 69.3 kg-CO2 per doughnut maker.
Beyond the effects of electricity generation, other major sources of CO2 emissions come from the production of metals (8%), transportation (8%), and the product’s manufacturing process itself (7%).
Electricity generation associated with this product accounts for more than half of all sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions, one of the chief chemicals contributing to acid rain. Truck transportation is responsible for the large quantity of Carbon Monoxide (CO) that is released into the atmosphere, a chemical that is characteristic of incomplete combustion.
Given the knowledge that electricity consumption has far more critical implications than the materials involved in creating the product, it seems unreasonable to attempt to change these. There are no particularly elaborate materials used and there are areas of consumer usage that would be ideal for environmental analysis and redesign.
The most significant improvement would come by reducing the electrical consumption per doughnut. This could be achieved by carrying multiple doughnuts through the oil simultaneously (instead of letting each doughnut cycle fully (~1 min) before the next doughnut is dispensed). This has the potential to reduce the time from 2+ hours to a matter of minutes without significantly affecting the production. Maintaining oil temperature and powering the conveyor belt for this duration is extremely energy intense. This time should be kept to a minimum.
Mechanical Analysis
Team Members & Roles
Michael Barako - DFE, Mechanical Analysis
Meng Yee Chuah - Mechanical Function
Katie McManus - Assembly Photos, DFMA
Sam Powers - Bill of Materials, FMEA
Sara Whitby - Executive Summary, Major Stakeholders, Usage and Usability