Floating
From DDL Wiki
m (→Limitations) |
(→Process) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=Process= | =Process= | ||
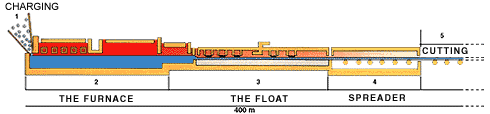
| - | Float glass is produced first by forming molten glass from raw materials, such as silica sand, calcium, oxide, soda, and magnesium. These raw materials are heated to approximately 1500 degrees Celsius within a furnace to form the molten glass. The molten glass then flows from the furnace onto a pool of molten tin, called a tin bath. The glass does not mix with the molten tin. Under the influence of gravity, the glass slowly flattens until both surfaces are perfectly flat. Finally, the molten glass is cooled to room temperature, resulting in the final product of a perfectly flat sheet of glass. | + | Float glass is produced first by forming molten glass from raw materials, such as silica sand, calcium, iron oxide, soda, and magnesium. These raw materials are heated to approximately 1500 degrees Celsius within a furnace to form the molten glass. The molten glass then flows from the furnace onto a pool of molten tin, called a tin bath. The glass does not mix with the molten tin. Under the influence of gravity, the glass slowly flattens until both surfaces are perfectly flat. Finally, the molten glass is cooled to room temperature, resulting in the final product of a perfectly flat sheet of glass. |
[[Image:verreplat_schema.gif|frame|Floating Glass Manufacturing Process]] | [[Image:verreplat_schema.gif|frame|Floating Glass Manufacturing Process]] | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 7 September 2007
Page under construction by:
Contents |
Process
Float glass is produced first by forming molten glass from raw materials, such as silica sand, calcium, iron oxide, soda, and magnesium. These raw materials are heated to approximately 1500 degrees Celsius within a furnace to form the molten glass. The molten glass then flows from the furnace onto a pool of molten tin, called a tin bath. The glass does not mix with the molten tin. Under the influence of gravity, the glass slowly flattens until both surfaces are perfectly flat. Finally, the molten glass is cooled to room temperature, resulting in the final product of a perfectly flat sheet of glass.
Advantages Over Other Methods
Limitations
The floating process can only create flat sheets of glass. However, other processes such as shearing can be used to cut this flat sheet into various shapes as necessary.
References
Created by Robert Gimson, Richard Hauffe, Chris Cavanaugh, Jon Bodnarik