Wet Etching
From DDL Wiki
Current revision (01:53, 14 February 2007) (view source) |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Group 9: Michael Kuo, Rikki Lam, Yun Han Luo, Gary Wu | Group 9: Michael Kuo, Rikki Lam, Yun Han Luo, Gary Wu | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[category:manufacturing]] | ||
Current revision
Wet etching is a manufacturing process where some chemical is used to dissolve unprotected metal in order to create designs on the surface. Usually, a metal plate is covered with an acid resistant film, sometimes referred to as a mask, and an artist will scrape off parts of the mask into a design. Once complete, the plate is dipped inside a container with an acid bath that will dissolve the unprotected portion of the material resulting in the intended design.
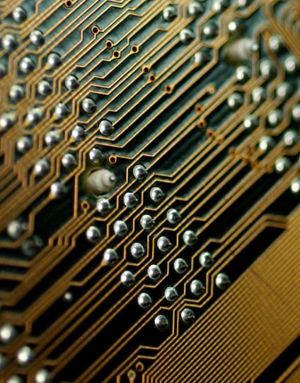
In design, etching is mainly used by artists to create master prints whose etched lines can be filled with ink and produce multiple prints. In industry, wet etching has been applied to the fabrication of printed circuit boards and semiconductors. Conductive pathways are etched onto a silicon wafer of a printed circuit board using copper sheets.
source:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Printed_circuit_board
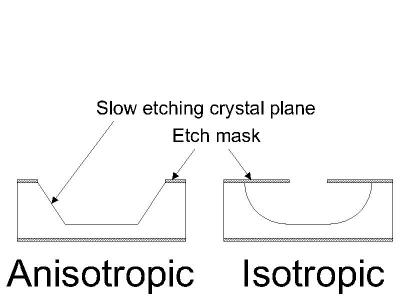
Wet etching is the simplest form of etching, only requiring a chemical that will dissolve metal at a rate faster then the mask. However, problems may arise depending on the pattern desired. Some materials, such as silicon, may exhibit anisotropic etching in certain chemicals where the singer crystal structure results in different etch rates in different directions of the material. As a result, the sides of the holes produced by the acid may be pyramid shaped instead of the intended rounded sided holes produced by isotropic wet etching.
source:http://www.memsnet.org/mems/processes/etch.html
In general, wet etching should be used when etching thin films on substrates or etching the substrate itself. Alternatively, dry etching can be used to cut vertical sidewalls if needed; however, dry etching can be twice as expensive.
see Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Etching
Sources:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Etching
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_etching
http://www.memsnet.org/mems/processes/etch.html
Group 9: Michael Kuo, Rikki Lam, Yun Han Luo, Gary Wu