Power scrubber
From DDL Wiki
(→DFA) |
(→Parts List) |
||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | | Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_sponge.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_sponge.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | | Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_velcro.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_velcro.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | | Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_1.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_1.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
| | | | ||
| Rubber | | Rubber | ||
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_rubber_1.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_rubber_1.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |PA6/G30 Plastic |
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_2.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_2.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |POM plastic |
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_cover.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_cover.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 167: | Line 167: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Steel |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_2.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_2.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 179: | Line 179: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_1.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_1.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 189: | Line 189: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Steel |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_4.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_4.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 201: | Line 201: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_housing.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_housing.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 211: | Line 211: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Steel |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_3.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_gear_3.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 222: | Line 222: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Multiple |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_motor.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_motor.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_motor_housing.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_motor_housing.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 245: | Line 245: | ||
| | | | ||
| Copper | | Copper | ||
| - | | | + | |Die Cutting and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_1.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_1.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 255: | Line 255: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Steel |
| - | | | + | |Extruding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_pin.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_pin.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 267: | Line 267: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS, Rubber | | ABS, Rubber | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_shell.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_shell.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 277: | Line 277: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Steel |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_screw.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_screw.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 288: | Line 288: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Multiple |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_circuit_board.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_circuit_board.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 300: | Line 300: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_circuit_board_housing.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_circuit_board_housing.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 310: | Line 310: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Plastic |
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_button.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_button.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 321: | Line 321: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Nickel Plated Copper |
| - | | | + | |Die Cutting and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_4.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_4.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 333: | Line 333: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_battery_housing_2.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_battery_housing_2.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 343: | Line 343: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Nickel Plated Copper |
| - | | | + | |Die Cutting and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_5.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_5.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 354: | Line 354: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Nickel Plated Copper |
| - | | | + | |Die Cutting and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_3.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_3.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 365: | Line 365: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Nickel Plated Copper |
| - | | | + | |Die Cutting and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_clicker.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_clicker.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 377: | Line 377: | ||
| | | | ||
| ABS | | ABS | ||
| - | | | + | |Injection Molding |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_battery_housing_1.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_battery_housing_1.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 387: | Line 387: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Nickel Plated Copper |
| - | | | + | |Die Cutting and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_2.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_conduction_2.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 398: | Line 398: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| - | | | + | |Steel |
| - | | | + | |Extruding and Bending |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_handle.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_handle.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 410: | Line 410: | ||
| | | | ||
| Rubber | | Rubber | ||
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_rubber_3.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_rubber_3.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
| Line 421: | Line 421: | ||
| | | | ||
|Rubber | |Rubber | ||
| - | | | + | |Off the Shelf |
| [[Image:Power_scrubber_rubber_2.jpg|100px|center]] | | [[Image:Power_scrubber_rubber_2.jpg|100px|center]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 21:58, 20 September 2012
Contents |
Exectuve Summary
Major Product Stakeholder Analysis
We identified four major categories of stakeholders for our product. They are manufacturers, shipping & transportation companies, retailers, and consumers.
Stakeholder Objectives
- Manufacturers
Low cost raw materials Simple manufacturing process required for materials chosen -- easy for mass production Energy efficient manufacturing process Recyclable materials Easy assembly Low cost packaging
- Shipping & transportation companies
Firmly packaged Light weight packaging Space efficient mass packaging
- Retailers
Appearance Cost Marketability (consumer needs) Durability
| Stakeholder Needs and Wants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stakeholder | Needs | Wants |
| Consumer |
|
|
| Retailer |
| |
| Manufacturer |
|
|
| Shipping & Transportation |
|
|
Product User Study
Mechanical Function
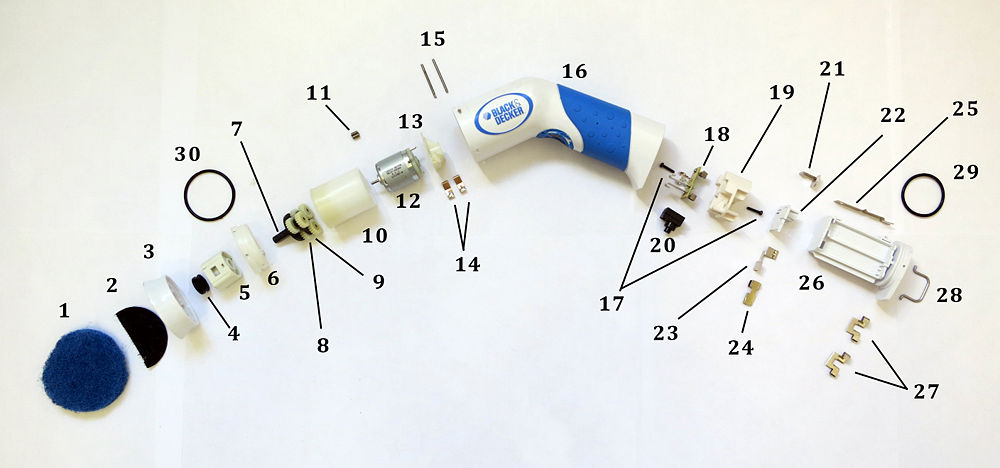
Parts List
| Part Number | Name | Quantity | Mass (g) | Subassembly | Function | Material | Manufacturing Process | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sponge | 1 | Off the Shelf | |||||
| 2 | Velcro | 1 | Off the Shelf | |||||
| 3 | Device Head | 1 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 4 | Rubber Ring #1 | 1 | Rubber | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 5 | Connector | 1 | PA6/G30 Plastic | Injection Molding | ||||
| 6 | Gear Cover | 1 | POM plastic | Injection Molding | ||||
| 7 | Planetary Gear #1 | 1 | Steel | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 8 | Planetary Gear #2 | 6 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 9 | Planetary Gear #3 | 1 | Steel | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 10 | Gear Housing | 1 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 11 | Gear on Motor | 1 | Steel | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 12 | Motor | 1 | Multiple | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 13 | Motor Housing | 1 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 14 | Conductor #1 | 2 | Copper | Die Cutting and Bending | ||||
| 15 | Pin | 2 | Steel | Extruding | ||||
| 16 | Outer Shell | 1 | ABS, Rubber | Injection Molding | ||||
| 17 | Screw | 2 | Steel | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 18 | Circuit Board | 1 | Multiple | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 19 | Circuit Board Housing | 1 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 20 | Button | 1 | Plastic | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 21 | Conductor #2 | 1 | Nickel Plated Copper | Die Cutting and Bending | ||||
| 22 | Battery Housing #1 | 1 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 23 | Conductor #3 | 1 | Nickel Plated Copper | Die Cutting and Bending | ||||
| 24 | Conductor #4 | 1 | Nickel Plated Copper | Die Cutting and Bending | ||||
| 25 | Clicker | 1 | Nickel Plated Copper | Die Cutting and Bending | ||||
| 26 | Battery Housing #2 | 1 | ABS | Injection Molding | ||||
| 27 | Conductor #5 | 2 | Nickel Plated Copper | Die Cutting and Bending | ||||
| 28 | Handle | 1 | Steel | Extruding and Bending | ||||
| 29 | Rubber Ring #2 | 1 | Rubber | Off the Shelf | ||||
| 30 | Rubber Ring #3 | 1 | Rubber | Off the Shelf |
Design For Manufacturing and Assembly
DFM
The product uses standardized components for many of the components such as the screws, motor, and Velcro, etc. For the ease of manufacturing, all the conducting metal pieces have similar dimensions; this means that fewer tools and setups are required during the manufacturing process. Most of the other customized parts are made of the same material, ABS, which are easy to work with using injection molding for mass production. Furthermore, since injection moldings are used for the ABS parts, not many finishing operations are needed to further reduce cost. The product uses the rubber rings as a multifunctional part what work as a seal for water proof as well as a locking mechanism for holding parts together. The rubber rings also help avoid tight tolerances based on its flexibility, which result in cost reduction. For the outer shell, special process of injecting two materials, rubber and ABS, are used to eliminate extra works for assembly.
There are also rooms for improvement. The product is composed of many small pieces in the interior of the device that could possibly be designed with fewer pieces. Also, although injecting molding can account for irregular shape, those small pieces can be modified into simpler shapes without losing their functionalities. The battery holder can be considered to be bought off the shelf and integrate with the product with minor design changes. The product uses soldering for connecting the motor to the conducting metals; however, it might be less cost and time consuming if the conducting piece can be redesign to secure the connection.
Overall, the design choices are made well for consideration of manufacturing. Limited materials are used for the components, they are chosen to be easily fabricated, and most of them do not require secondary and finishing operations. Although injecting molding can be expensive, the product is mass produced, which cut down the cost for every extra part produced. On the other hand, it may be possible to reduce the numbers of parts by combining subassembly into one component, which can make the design simpler. It is also important to consider the cost of using special process property as oppose to assembling after the parts are manufactured.
DFA
The product only requires two pins and two screws in the whole assemble and the outer shell only consists of one piece. One example of eliminating the use of screws in assembling is the snapping mechanism used for closing the gearbox. Another example is using rubber as a way to lock the battery housing in place. The product consists multiple subassemblies, such as the battery housing, the circuit board, and the motor/gear set. Each component is designed in certain shapes to prevent mistakes in assembly orientation. The way the circuit board subassembly comes in contact with the motor subassembly is one example. The assembly directions are minimized to two and components either go in from top or bottom. The openings also have different shapes to help recognizing what goes where. Furthermore, the outer shell provides guides on the interior wall for subassemblies to slide and fit in easily.
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
| Item and Function | Failure Mode | Effects of Failure | S | Causes of Failure | O | Design Controls | D | RPN | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Housing | Battery housing comes loose | No Power Source | 4 | Not closing properly | 4 | Scrubber would not turn on | 2 | 32 | A better clicking mechanism |
| Button: ON/OFF | Button sticks | Can't turn on or can't turn off | 4 | Alignment of button | 2 | Scrubber would not turn on | 1 | 8 | Make it a flip switch |
| Outter Shell | Cracking | No longer water proof | 4 | Dropping, crushing, overheating | 5 | Scrubber would not turn on | 2 | 40 | Coat entire body with rubber |
| Rubber gripping/waterproofing | Melts or wear and tear | No longer waterproof | 3 | Heat | 2 | Scrubber would not turn on | 3 | 18 | Better material choice |
| Motor-circuit board connection | Welding of copper loosens | Motor does not run | 4 | Fatigue, Overheating | 1 | Scrubber would not turn on | 3 | 18 | Better mesh of the motor with the circuit board |
Design For Environment
| Production | Use | Use | Use | Use | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item purchased | Power Scrubber Manufacturing | Battery | Sponge | Soap | Water |
| a) Picture | |||||
| b) Economic Sector Name and # | Small Electric appliance #335210 | Primary battery manufacturing #335912 | Broom, brush, and mop manufacturing #339994 | Soap and cleaning compound manufacturing #325610 | Water, sewage and other systems #221300 |
| c) Reference Unit | 1 item | 4 batteries | 1 piece | 16 oz/bottle | 19.5 gallon/day |
The Team
Team Leader: Xin (Pam) Hu
DFMA Leader: Ken-Soh (Robert) Mai
FMEA Leader: Ben Antoine
DFE Leader: Kelle Patterson
User Study Leader: Shao-Chuan (Ted) Fang